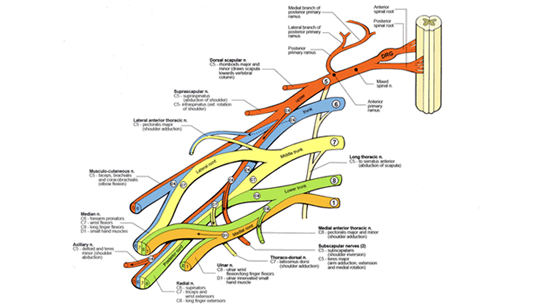
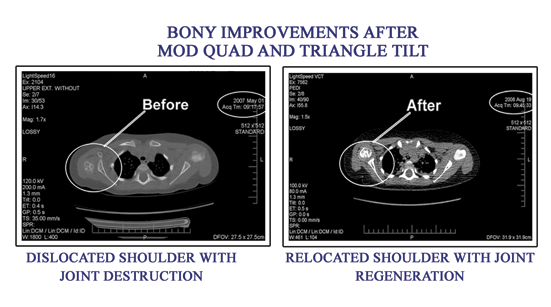
|
Primary Surgery FAQ
- When and how do you make the final determination that a child needs primary / nerve surgery?
- What type of therapy is appropriate while we wait and to see if surgery needed ? Pin sleeve to the chest? What type of ROMS - how often? Stretching?
- Can the nerve find an "alternate" path without primary surgery?
- Are there any tests we should have done locally before we come for a consultation?
- When is the best age to do primary surgery if the child has no hand/wrist/ or finger movement and why?
- When is the best age to do primary surgery if the child has no shoulder or elbow movement and why?
- What risks are associated with this surgery?
- Is there a chance my child can become worse after surgery?
- What will you do if you find an avulsion? Multiple avulsions?
- What will you do if you find a neuroma?
- What determines that a nerve graft should be done?
- Are there better places than others to take donor nerve from and why?
- How long does primary surgery take?
- I read that you patented a tool that is used for nerve grafting - can you explain what this is and how it helps you do this surgery?
- How will the child be immobilized after surgery, what type of immobilization and for how long?
- How do we follow-up with you after surgery if we are not from Houston?
- When do we begin therapy again after surgery?
- Do you have therapy protocols I can give our PT/OT?
- When will we see results and how will we know if the primary surgery worked?
- Is primary surgery ever repeated?
- We have been told by another clinic that nerve grafting surgery doesn't help the child gain any function. What is your opinion about this?
When and how do you make the final determination that a child needs primary / nerve surgery? back to top
In general, if there is no function in the shoulder and biceps to lift the part against gravity (with the child sitting up), I recommend exploratory surgery by age 4-6 months of age. If the hand is also paralyzed, then surgery should be earlier, 3-4 months if possible. Bending the arm and moving the shoulder while lying down is not a good indicator of function as gravity is eliminated in this position.
What type of therapy is appropriate while we wait and to see if surgery needed ? Pin sleeve to the chest? back to top
No immobilization; range of motion therapy is important to keep joints supple as well as to improve sensory integration. What type of ROMS - how often? Very gentle ROM of the shoulder and hand. 3-4 times a day if possible. Aggressive abduction of the arm and shoulder may cause inferior dislocations of the shoulder, so this should be avoided; also, aggressive stretching of the elbow can dislocate the radial head, again causing problems. Gentle ROM is best, and certainly nothing that causes crying or pain for the child. Stretching? Very careful stretching is OK, avoiding the shoulder and elbow if possible.
Can the nerve find an "alternate" path without primary surgery? back to top
That may be possible, although hard to imagine with very severe injuries. The main issue with timing of surgery is that if the nerves do not find an alternate pathway or if there is no surgery done with ruptured and avulsed nerves, paralysis will be permanent within 15 to 18 months. After that time, surgical correction is possible, but much more difficult and with poorer outcomes.
Are there any tests we should have done locally before we come for a consultation? back to top
An EMG (electromyogram ) test is very useful in determining the site and severity of injury. However, the clinical examination by a specialist is more important overall. MRI tests are sometimes ordered by local physicians but are generally not reliable in imaging brachial plexus injuries.
When is the best age to do primary surgery if the child has no hand, wrist or finger movement and why? back to top
Probably 2-3 months of age because it will take longer for the nerves to regenerate all the way from the neck area (where the injury is) down to the hand. Also, these tend to be much more severe injuries, so there is less chance of spontaneous recovery.
When is the best age to do primary surgery if the child has no shoulder or elbow movement and why? back to top
Around 4-6 months, because this will allow recovery if nerve grafting is needed, yet still give the longest time for spontaneous recovery to occur.
What risks are associated with this surgery? back to top
There are general risks present for any surgery such as infection, scarring, bleeding, allergic reactions, blood clots and even organ injury or death from anesthetic. The specific risks of nerve surgery are failure to work, possible worsening of function, numbness, weakness, and loss of function. In my practice, these have been very rare to negligible. I cannot think of a case made worse by primary surgery in my series of over 1,200 cases.
Is there a chance my child can become worse after surgery? back to top
There are slight possible chances for this to happen, but I have not seen this in my series of patients.
What will you do if you find an avulsion? Multiple avulsions? back to top
Avulsion injuries cannot be repaired directly to the spinal cord. However, nerve transfer procedures can be used to shunt healthy nearby nerves to the injured nerve and give function in this way. This link may help to understand the principles of nerve transfers: http://www.drnathbrachialplexus.com/images/pdf/new_nerve_transfers.pdf
What will you do if you find a neuroma? back to top
A neuroma is a mixture of regenerating nerves and scar tissue being formed at the site of injury to a nerve. The neuroma is tested in the operating room to see if there is some intact nerve passing through it. If there is some intact nerve, then based on the testing, the scarred parts are removed and the intact parts are preserved. If there is little or no nerve getting through the neuroma, then the entire neuroma is cut out. In both situations, the removed areas are replaced with healthy donor nerve taken from elsewhere in the body.
What determines that a nerve graft should be done? back to top
Mostly clinical and intraoperative testing. In my opinion, I like to see actual movement of the muscle being tested rather than just a signal on a machine. If there is enough movement to move the msucle against gravity when its nerve is stimulated, then I will generally not do a nerve graft.
Are there better places than others to take donor nerve from and why?
back to top
The donor nerve is virtually always taken from the sural nerve in the calf. This is a sensory nerve that can safely be removed without causing any movement deficits in the leg and leaves sensory feeling on the sole of the foot intact. If less nerve is needed, then it can be taken from the sensory nerves of the neck, again, with no deficit of function.
How long does primary surgery take? back to top
It usually takes me about 3-5 hours, depending on what specifically is needed and how severe the injury is.
I read that you patented a tool that is used for nerve grafting - can you explain what this is and how it helps you do this surgery? back to top
The United States patent is for a device that helps to suture nerves in difficult areas of the body, such as close to the spinal cord in brachial plexus injuries, and in the chest and abdomen. The idea is to replace tying knots with special clips that are easier and more precise to use.
How will the child be immobilized after surgery, what type of immobilization and for how long? back to top
The child is usually in a soft brace that holds the arm to the side for 2 weeks. Range of motion is performed every day on the elbow and hand.
How do we follow-up with you after surgery if we are not from Houston? back to top
The baby will stay in the hospital for 2 nights following surgery. This is to make sure that pain medication and antibiotics are given and so that the therapists can make a splint to fit and to teach wound care. Note that usually pain medication is not needed after the first 24 hours. The child is discharged home after 2 nights in the hospital, and then is seen by the local pediatrician for a wound check 3-4 days later. Follow-up with me is done through therapist's reports, regular videotape mailings, and through satellite clinics that I run in many states. Locally, a pediatrician may be important for prescriptions and other referrals, but generally I can organize this through my office. Note that this system has worked very well with several thousand patients over the past 8 years.
When do we begin therapy again after surgery? back to top
Within 2-3 weeks.
Do you have therapy protocols I can give our PT/OT? back to top
Pre-printed sheets will be sent home after surgery. These should be online on my website in the near future.
When will we see results and how will we know if the primary surgery worked? Will we have to have another EMG done and if so when? back to top
Usually results of the surgery are seen within 6-8 months and strength continues to improve over the next 2-3 years. Another EMG is sometimes required if the recovery is slower than expected to confirm that the nerves are growing in the right direction and restoring function.
Is primary surgery ever repeated? back to top
Sometimes, in less than 10% of cases, additional nerve surgery may be needed if the initial nerve grafts did not work or worked only partially. This would be in the form of a nerve transfer, not repeated nerve grafts.
We have been told by another clinic that nerve grafting surgery doesn't help the child gain any function. What is your opinion about this? back to top
My particular views on nerve grafting are based on experience with several thousand children, and I believe that in appropriate cases, nerve grafting is essential. Recovery of functional movements has been very reliable. I expect that other surgeons with different experiences might have different opinions, but overall the validity of nerve grafting has stood the test of time and most surgeons would agree that they are useful.
|