|
Anatomy of the Injury (Brachial Plexus Injury)
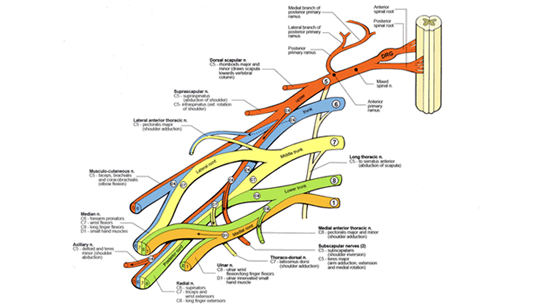
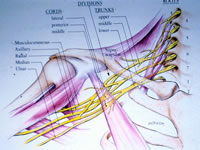
Brachial
plexus anatomy is complex, but can be described in terms
of basic function. The brachial plexus is derived
from 5 "roots" or spinal nerves that exit the
spinal cord in the neck. The nerves then pass through the
axilla or armpit behind the collarbone (clavicle), and split
into the final nerve branches that supply the muscles and
skin of the shoulder, arm, elbow and hand.
The roots are named
for the level of spinal cord that they exit.
The upper roots (C5 and C6) exit from the cervical
(meaning "neck") 5th and 6th vertebrae.
The middle root (C7) exits above the 7th cervical
vertebrae, and the lower roots exit from C8 (below
the 7th cervical vertebra) and T1 (below the 1st thoracic
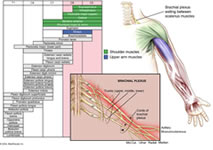
vertebra). The upper roots supply upper structures
(C5 to shoulder, C6 and C7 to elbow), and the lower
roots supply the forearm and hand. |
|
|
Injury to upper roots (the most common injury) is known as Erb’s palsy after the physician who described it. Erb’s palsy (paralysis) affects the shoulder and elbow, because the upper roots supply these structures. Injury to the lower roots is known as Klumpke’s paralysis, but is relatively uncommon, and very rarely exists by itself. Because the lower roots are injured, the hand is predominantly affected. If the lower roots are injured, the injury is generally so severe that all the roots of the plexus are involved, and the injury includes all parts of the arm. Upper root (Erb’s) injury is seen about 60% of the time, isolated Klumpke’s perhaps 5% of the time, and mixed injuries involving all elements of the plexus to some degree, make up 35% of patients. |
 |
The mechanism of injury
to the upper roots
is thought to be a bending or stretching of the neck
in a direction away from the side of injury.
Lower root injury is thought to be caused by pulling
up of the arm above the head, so that stretch on the
C8 and T1 roots results. Injuries can occur in both
children and adults, and similar mechanisms are apparently
responsible.
|
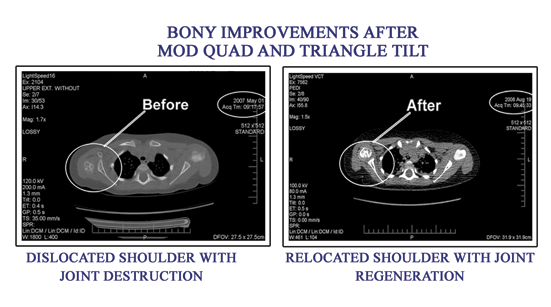
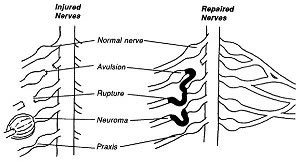
The upper roots happen to be firmly fixed to the bony sides of the spine, and so they tend to be torn in this region. These injuries can be repaired in a relatively straightforward manner.
Lower roots by circumstances of anatomy do not have support by bony structures, and therefore are unprotected and tend to be torn out of the spinal cord. These injuries cannot be directly repaired and other techniques of reconstruction must be employed. |
Contact US
|