|
Adult Injury
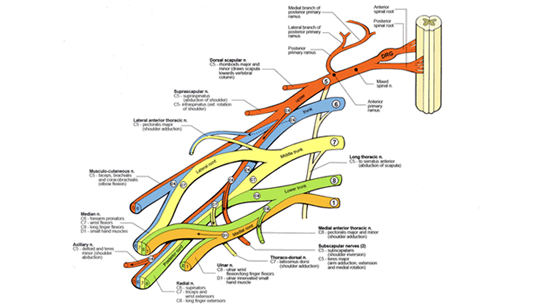
Most adult injuries to the brachial plexus occur as a result of significant trauma such as during a motor vehicle accident. Motorcycle and all-terrain vehicles are most commonly involved although automobile accidents can also cause the injury. Typically, the head and neck are forced away from the shoulder and arm, thus stretching the nerves of the brachial plexus and resulting in tearing, rupture and avulsion if the force is great enough. Injury can also occur in adults as the result of inflammation (Parsonage- Turner Syndrome, or brachial neuritis), tumor, radiation and other causes.
The treatment of adult injuries follows certain principles:
(1) Nerve repair if needed should take place before 6- 7 months after onset of injury to get the best chance of functional improvement.
(2) The distances for nerve regeneration to occur are of course greater in adults than in children due to their limb length; therefore, nerve transfer surgical techniques rather than nerve grafting in the neck are more often utilized. Nerve transfer is the use of a donor nerve to supply the power for an injured nerve. Nerve grafting is the use of bridge nerves to reconstruct the originally injured nerve. Because nerve transfers are performed closer to the denervated muscle than nerve grafts, the distances for regeneration are greatly reduced and recovery of function should occur in a shorter time frame
(3) Surgery tends to be recommended between 4- 6 months after injury, because of regeneration distances. Atrophy of the denervated muscles occurs more quickly in adults.
(4) Pain due to the nerve injury itself is more common in adults than in children; this may be due to a greater incidence of root avulsion injury. Adults often need further surgical procedures such as spinal cord stimulation, sympathectomy or dorsal root entry zone (DREZ) lesions for pain control
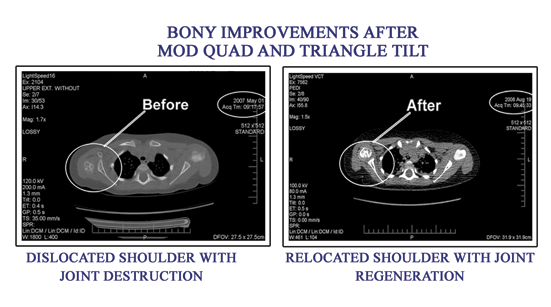
(5) Although major nerve injuries, including brachial plexus injuries, do cause reduction in limb size and contractures in adults, the same degree of injury in children results in greater deformity. This is due to the fact that growth of the bones and other structures of the arm and hand is dependent on an intact nerve supply. In adults, common areas for contracture are the chest and armpit area, the elbow, the forearm and the large knuckle joints of the hand. All can be helped with physical therapy to some extent, but surgical release of contractures, tendon transfers and nerve decompression are used frequently.
|
Contact US
|